Every four years, Bitcoin experiences an event that rocks the crypto market: Bitcoin halving. It’s more than simply a technical adjustment; it’s a fundamental process that controls supply, impacts market mood, and frequently sparks dramatic price rises.
The halving schedule of Bitcoin, the world’s largest cryptocurrency, is critical in establishing its economic structure and investor behavior. But what precisely is Bitcoin halving, and why is it important to everyone, from miners to institutional investors?
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
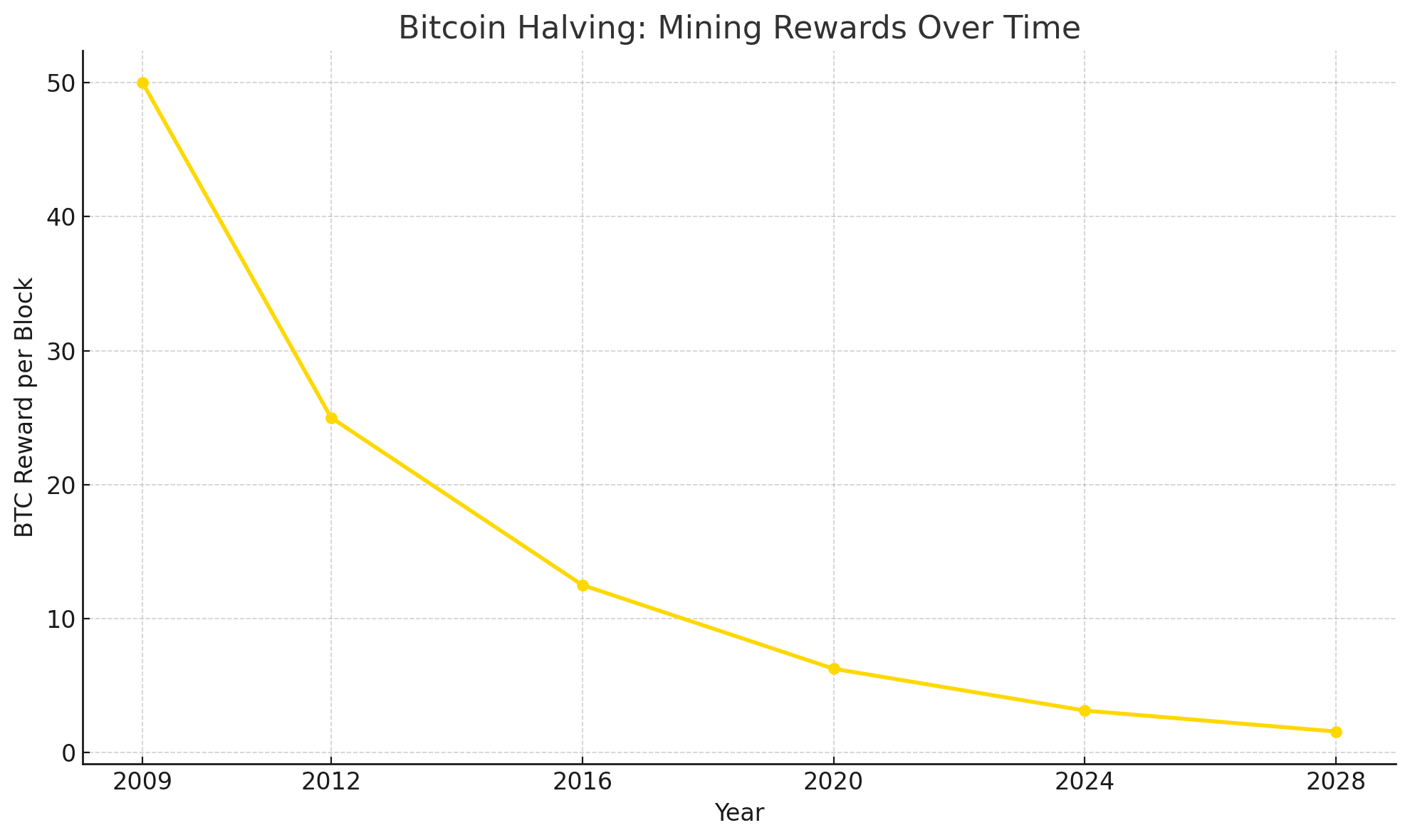
Bitcoin halving is a planned occurrence in which miners earn a smaller reward for confirming transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. Originally, miners received 50 BTC every block. This award is reduced in half with each halving. The most recent halving took place in April 2024, lowering the reward from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC per block.
Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, programmed this process into the protocol, and it will continue until the maximum quantity of 21 million BTC is achieved. The next halving is scheduled for 2028, and it will further cut mining earnings to 1.5625 BTC. This scarcity model resembles deflationary assets like as gold, bolstering Bitcoin’s status as “digital gold.”
“Halving is Bitcoin’s heartbeat,” stated one blockchain economist. “It recalibrates supply and incentivizes long-term holding, reinforcing Bitcoin’s value proposition.”
Why Bitcoin Halving Matters for Price
Historically, Bitcoin halving has resulted in considerable price hikes. Following the 2012 halving, Bitcoin skyrocketed from $12 to more over $1,000. After 2016, it increased from $650 to roughly $20,000 in a year. The 2020 halving drove a bull run, bringing Bitcoin close to $70,000 by late 2021.
The answer is simple economics: when the supply of a valued asset falls while demand remains constant or grows, the price rises. Bitcoin halving slows the pace at which new coins enter circulation, resulting in a supply shock. This occurrence frequently serves as a trigger for speculative purchases, institutional entrance, and retail FOMO (fear of missing out).
Trading volumes soared in 2024, only weeks after the most recent halved, and long-term holders boosted their accumulation, indicating that market players saw halving as a favorable occurrence.
The Impact on Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin miners are directly affected by the halving, since their block rewards are reduced in half. This is a hurdle, particularly for small or inefficient mining operations. With less BTC produced every block, miners must rely on transaction fees or cut operating costs to be viable.
This dynamic frequently results in miner capitulation, in which less lucrative miners close down, followed by a transfer of hash power to bigger, more efficient players. However, the technique improves Bitcoin mining security and competitiveness over time.
Major mining companies have already begun updating their equipment and relocating to places with cheaper power prices in expectation of diminished revenues. “Miners must double down on efficiency and strategy. In a recent interview, a mining executive stated that halving incentives is a reality for which they are preparing years in advance.
Long-Term Significance of Bitcoin Halving
Beyond short-term price movements and mining economics, Bitcoin halving reinforces the cryptocurrency’s scarcity myth. With each halving, Bitcoin’s inflation rate falls dramatically, making it more enticing in a macroeconomic climate characterized by fiat currency creation and growing inflation worries.
This predictable and transparent monetary strategy contrasts with central bank-controlled fiat currencies. Investors are increasingly viewing Bitcoin’s halving as a sign of financial discipline, particularly as geopolitical uncertainty and monetary easing continue to dominate global finance.
Some observers anticipate that the next few halving cycles will coincide with increased use of Bitcoin ETFs, greater participation from sovereign investors, and increased integration into traditional finance. This reinforces why Bitcoin’s halving remains one of the most significant events on the crypto calendar.
Conclusion: A Built-In Catalyst for the Future
Bitcoin halving is more than simply a function; it is a concept built into the network. It guarantees a consistent scarcity, balances mining incentives, and influences long-term market behavior. For investors, it’s a sign of possible opportunity; for miners, it’s time to react.
For the crypto sector as a whole, the Bitcoin halving is a one-of-a-kind event that combines economic theory with decentralized innovation. Each halving limits Bitcoin’s output, increasing the value of each coin, not just monetarily, but also symbolically.
Read about Bitcoin ETF as well.
FAQs
What is Bitcoin halving in simple terms?
Bitcoin halving is when the reward for mining new BTC blocks is cut in half, reducing the rate of new coin creation.
How often does Bitcoin halving happen?
Approximately every four years or after every 210,000 blocks.
Does Bitcoin halving always increase price?
Historically, yes, but there are no guarantees. It depends on demand, market conditions, and macroeconomic factors.
Is Bitcoin halving good for investors?
Many long-term investors see it as a bullish signal due to reduced supply and potential price growth.
Glossary of Key Terms
Bitcoin Halving: A scheduled event that reduces Bitcoin mining rewards by 50%.
Mining Reward: BTC earned by miners for validating blockchain transactions.
Supply Shock: A sudden drop in the availability of an asset, often leading to price increases.
Hash Power: The total computational power used to mine and process transactions on the Bitcoin network.
Block: A group of Bitcoin transactions that gets added to the blockchain.